Blhaj, Khaled Mohamed Salem (2014) THE EFFECT OF EVOO IN REDUCING ICAM-1 AND INCREASING e-NOS IN HIGH FAT DIET RATS. Masters thesis, Master Program of Biomedical Science.
| PDF - Published Version 7Mb | |
| PDF (Chapter 1) - Published Version 7Mb | |
| PDF (Chapter 2) - Published Version 7Mb | |
| PDF (Chapter 3) - Published Version 7Mb | |
| PDF (Chapter 4) - Published Version 7Mb | |
| PDF (Chapter 5) - Published Version 7Mb | |
| PDF (Chapter 6) - Published Version 7Mb | |
| PDF (References) - Published Version 7Mb | |
| PDF (Appendixes) - Published Version 7Mb |
Abstract
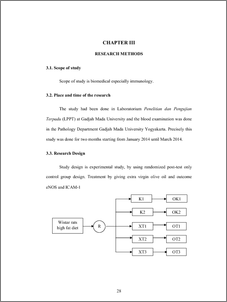
Background: High fat diet (HFD) induces low chronic inflammation andsubsequently leads to the development of endothelial dysfunctions, which are considered as the first pathological symptom of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is marked by increasing sICAM-1 and decreasing eNOS levels, which both of them released by endothelial cells. Consuming EVOO having anti-inflammation effect may retain normal endothelial functions. This study therefore aimed to prove the effect of EVOO in maintaining endothelial cells of wistar rats during HFD consumption. Methods: A randomized post-test only control group design was performed on wistar rats, which were divided into 5 groups, every group consists of 6 rats. Negative and positive control groups received normal diet and HFD, respectively. Three treated groups received combination of HFD and EVOO in different dose (1ml, 2ml, and 3ml/kg BW/day, respectively) for period of 60 days. Serum ICAM-1 and eNOS levels were measured using ELISA method. Results: No significant different of ICAM-1 levels (ANOVA test; p=0.202), but significant different of eNOS levels were observed among all groups studied (ANOVA test; p=0.001). Further analysis proved that the eNOS levels of positive controls (mean ± SD; 0.32±0.14 ng/ml) were significantly lower than those of negative controls (0.72±0.32; p=0.006) and group of HFD rats receiving EVOO in dose of 3ml/kg BW/day (1.01±0.45; p=0.022). Post Hoc tests of serum eNOS levels between other groups were not significantly different. Conclusions: The result of this study indicates that all conducted treatments have no effect on ICAM-1 levels. Unlike EVOO (3ml/kg BW/day) able to improve eNOS levels of HFD rats. Key words: EVOO, HFD, ICAM-1, eNOS.
| Item Type: | Thesis (Masters) |
|---|---|
| Subjects: | R Medicine > R Medicine (General) |
| Divisions: | School of Postgraduate (mixed) > Master Program in Biomedical Science |
| ID Code: | 48502 |
| Deposited By: | INVALID USER |
| Deposited On: | 08 Apr 2016 14:30 |
| Last Modified: | 08 Apr 2016 14:30 |
Repository Staff Only: item control page