Nugraha, Widya Eka (2015) MOLECULAR ANALYSIS OF INDONESIAN LCA PATIENTS AND IN VITRO SPLICE CORRECTION FOR CEP290-ASSOCIATED LCA. Masters thesis, Master Program of Biomedical Science.
| PDF (Cover) - Published Version 378Kb | |
| PDF (Chapter 1) - Published Version 107Kb | |
| PDF (Chapter 2) - Published Version 461Kb | |
| PDF (Chapter 3) - Published Version 244Kb | |
| PDF (Chapter 4) - Published Version 604Kb | |
| PDF (Chapter 5) - Published Version 218Kb | |
| PDF (Chapter 6) - Published Version 185Kb | |
| PDF (Chapter 7) - Published Version 194Kb | |
| PDF (References) - Published Version 115Kb | |
| PDF (Appendix) - Published Version 273Kb |
Abstract
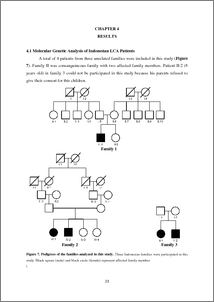
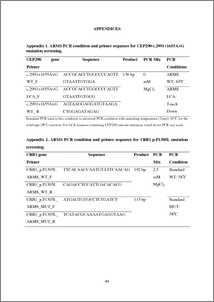
Background: Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA) is an autosomal recessive retinal disorder, characterized by an early-onset visual loss, amaurotic pupils, and retinal degeneration. Only a few studies have been described about Indonesian LCA patients. Pre-clinical studies have shown that antisense oligonucleotide (AON) restored the aberrant splicing caused by a recurrent intronic mutation in the CEP290 gene. This study combined diagnostic study in Indonesian LCA patients and in-vitro AON-based therapy for LCA. Methods: CEP290, CRB1, GUCY2D, and AIPL1 genes were screened in 4 LCA patients from 3 unrelated families by amplification refractory mutation system (ARMS) PCR or Sanger sequencing. Meanwhile, 29 different AONs (GT1 to GT29) with two chemistries were designed and tested by RT-PCR, Western blot, and immunocytochemistry. Results: Three variants were found in AIPL1 gene: p.E318G, p.R324R, and p.G11G. Interestingly, p.E318G was predicted as a disease causing mutation by MutationTaster program while p.R324R and p.G11G were predicted to cause a splicing alteration by ESE-finder splicing prediction. On the other hand, from 29 AON tested in this study, 4 AONs worked efficiently in correcting the aberrant splicing, increasing the CEP290 protein, and restoring the cilium length, at low concentrations. Conclusions: The molecular genetic analysis of Indonesian LCA patients in this study revealed three new candidate variants as a LCA causative mutation in AIPL1: p.E318G, p.R324R, and p.G11G. From 29 AONs tested in this study, GT2, GT3, and GT4 were the most efficient. Remarkably, these AONs shared the same chemical modification. Keywords: Leber congenital amaurosis, splicing mutation, antisense oligonucleotide, CEP290
| Item Type: | Thesis (Masters) |
|---|---|
| Subjects: | R Medicine > R Medicine (General) |
| Divisions: | School of Postgraduate (mixed) > Master Program in Biomedical Science |
| ID Code: | 46670 |
| Deposited By: | INVALID USER |
| Deposited On: | 29 Oct 2015 09:30 |
| Last Modified: | 29 Oct 2015 09:30 |
Repository Staff Only: item control page