M.S Nairat, Muath (2012) PROTECTIVE EFFECTS OF NIGELLA SATIVA EXTRACT ON ETHANOL INDUCED HEPATIC TISSUE DAMAGE AND TNFα EXPRESSION (Experimental Study In Wistar Rats). Masters thesis, Diponegoro University.
| PDF (Cover) - Published Version 226Kb | |
| PDF (Chapter 1) - Published Version 216Kb | |
| PDF (Chapter 2) - Published Version 542Kb | |
| PDF (Chapter 3) - Published Version 179Kb | |
| PDF (Chapter 4) - Published Version 1092Kb | |
| PDF (Chapter 5) - Published Version 123Kb | |
| PDF (Chapter 6) - Published Version 90Kb | |
| PDF (Reference) - Published Version 159Kb | |
| PDF (Appendix) - Published Version 461Kb |
Official URL: http://mbiomedik.undip.ac.id/
Abstract
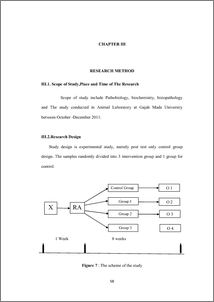
Background: Alcohol intake causes fatty liver, liver tissue inflammation, and liver cirrhosis, Nigella sativa seeds had been reported with anti-inflammatory effect. Objective: To identify and analyze the protective effect of Nigella sativa extract on alcohol induced liver damage in wistar rats. Method: This experimental study used randomized post-test control group design in 24 male Wistar rats divided into four groups each group contain 6 rats, control group given ethanol 8mg/kgBW/day for 8 weeks, group1 ,group 2,group 3, given Nigella sativa extract plus ethanol after one hour for 8 weeks as 0.5 g/kgBW/day, 1 g/kgBW/day, 1.5 g/kgBW/day respectively, ethanol dose 8mg/kgBW/day, the liver tissue were H&E stained and observed for liver cell changes , Imunohistochemistry was done to count the percentage of TNFα in Cytoplasm stained brown color and the intensity of the staining then its classify according to Allred Score. Result: There was severe, moderate, mild and normal liver tissue for control, group1, group2,and group3 respectively the difference among groups and between each group were statistically significant (p=0.00), except between control group and group 1 (P=0.093) for the liver tissue damage, there was 3 Allred,2 Allred, 1 Allred and 0 Allred for control, group1, group2, group3 respectively the difference among groups and between all groups was statistically significant (p=0.00) for TNFα expression. Conclusion: Nigella sativa extract shows protective anti-inflammatory effect, as reducing the damage change and the TNFα expression in hepatocye that induced bu ethanol . Keywords: ethanol, liver tissue damage, TNFα
| Item Type: | Thesis (Masters) |
|---|---|
| Subjects: | R Medicine > RB Pathology |
| Divisions: | School of Postgraduate (mixed) > Master Program in Biomedical Science |
| ID Code: | 35603 |
| Deposited By: | INVALID USER |
| Deposited On: | 22 Jun 2012 08:31 |
| Last Modified: | 22 Jun 2012 08:31 |
Repository Staff Only: item control page