Harlina , Ihah (2005) Analisis besi dalam air sumur menggunakan metode uji noda. Undergraduate thesis, FMIPA UNDIP.
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 1755Kb | ||
| PDF 16Kb | |
| PDF 370Kb | |
| PDF 517Kb | |
| PDF 364Kb | |
| PDF 625Kb | |
| PDF 625Kb | |
| PDF 462Kb | |
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 756Kb | ||
| PDF 322Kb | |
| PDF 333Kb | |
| PDF 364Kb |
Abstract
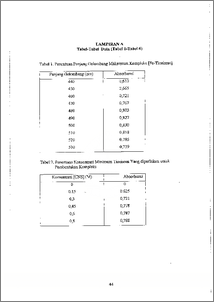
Besi merupakan salah satu unsur kimia yang terdapat hampir di setiap tempat di bumi, yang salah satunya adalah perairan. Besi dalam perairan berada dalam bentuk fero (Fe24) dan feri (Fe3+). Menurut standar Baku mutu air, batas maksimum kadar besi yang diperbolehkan untuk air minum adalah 1 ppm. Secara estetika jika konsentrasi besi terlalu tinggi maka akan menimbulkan noda khususnya pada kain dan porcelin. Besi dalam penyimpanan cenderung tidak stabil sehingga diperlukan analisis langsung. Uji nods merupakan metoda analisis untuk mengidentifikasi logam dalam suatu sampel dengan melihat perubahan wama yang dihasilkan. Penelitian telah dilakukan untuk mengidentifikasi dan menentukan kandungan besi dalam sampel serta mengetahui interaksi antara silika gel dengan zat pengompleks. Sampel yang digunakan adalah air sumur di daerah Banjarsari Selatan Tembalang Semarang. Uji noda dilakukan pada silika gel dan kertas caring menggunakan zat pengompleks o-Fenantrolin dan tiosianat. Ion fero (Fe24) bereaksi dengan orto-Fenantrolin membentuk kompleks [(C121-18142)3Fej2+ yang berwarna merah-orange dan ion feri bereaksi dengan tiosianat membentuk kompleks [Fe(SCN)6r yang berwarna merah. Kemudian untuk mengetahui interaksi silika gel dengan zat pengompleks, silika gel dikerok dari plat uji dan dianalisis dengan FT1R. Dari hasil penelitian menggunakan metoda uji noda diperoleh kandungan besi dalam sampel berada pada daerah 6-9 ppm dan dari hasil analisis FTIR dapat disimpulkan bahwa interaksi yang terjadi antara silika gel dengan zat pengompleks merupakan adsorpsi fisik. Iron is one of the chemical element which is exist almost everywhere on earth, the one is in waters. Iron in the water solutions form salt of ferrous iron (Fe2+) and ferric iron (Feat). Based on standard water quality, maximum limit iron which permitted for drinking water is I ppm. As an aesthetics manner, if iron concentration very high, will cause staining of laundry and porcelin. Iron in the solutions inclined not stable, so need direct analysis. Spot test is an analysis method to identify metal in a sample by observed colour exchange that appeared. This experiment was done to identify and to determine iron contents in a sample and to know the interaction between silica gel with complex agent. Sample which used is potable ground water at Sourth Banjarsari Tembalang Semarang. Spot test was done at silica gel plate and filter paper using ortho¬phenanthroline and thiocyanate as complex agent. Ferrous iron (Fe2+) to reacted with ortho-phenanthroline (C12H8N2) formed [(C12H8N2)3Fe]2+ orange-red complex and ferric iron to reacted with thiocyanate formed [Fe(SCN)6]i- red complex. To know the interaction between silica gel with complex agent, silica gel was scraped from test plat and analyed by FTIR. Result of this experiment using spot test method, iron contents of sample is range between 6-9 ppm and from FTIR analysis can be concluded that the interaction between silica gel and ortho-phenanthroline is a physical adso
| Item Type: | Thesis (Undergraduate) |
|---|---|
| Subjects: | Q Science > QD Chemistry |
| Divisions: | Faculty of Science and Mathematics > Department of Chemistry |
| ID Code: | 31040 |
| Deposited By: | Mr UPT Perpus 1 |
| Deposited On: | 14 Nov 2011 07:57 |
| Last Modified: | 14 Nov 2011 07:57 |
Repository Staff Only: item control page