R u s e n o , R u s e n o (2005) Piroksis dan piroksi katalis campuran plastik dan tempurung kelapa menjadi hidrokarbon cair. Undergraduate thesis, FMIPA UNDIP.
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 2054Kb | ||
| PDF 32Kb | |
| PDF 364Kb | |
| PDF 440Kb | |
| PDF 366Kb | |
| PDF 579Kb | |
| PDF 377Kb | |
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 576Kb | ||
| PDF 323Kb | |
| PDF 374Kb | |
| PDF 998Kb |
Abstract
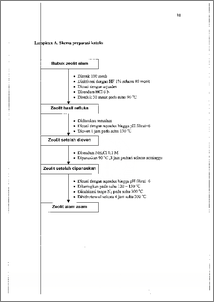
Penggunaan plastik • dalam kehidupan yang terus meningkat mengakibatkan mel mpahnya sampah plastik. Salah satu plastik yang banyak digunakan dibuat dan poll -tilen. Sementara itu, pengolahan kelapa menghasilkan limbah tempurung yang me gandung selulosa (36,3 %), lignin (28,3 %) dan hemiselulosa (25,1 %) yang ber otensi untuk diolah secara kimia. Tujuan pirolisis campuran plastik—tempurung kel pa ini adalah untuk menentukan pengaruh komposisi plastik—tempurung kelapa sert: katalis terhadap produk pirolisis. Pirolisis dilakukan terhadap 60 g campuran plastik—tempurung kelapa dengan per n andingan massa 1 : 5, 1 : 2, 1 : 1, 2 : 1 dan 5 : 1 pada suhu 300 °C dalam reaktor bate h. Untuk pirolisis katalitik, 5 g katalis zeolit alam asam ditambahkan ke dalam rea tor. Kondisi inert diperoleh dengan mengalirkan gas N2 ke dalam reaktor. Gas hasilpirolisis didinginkan dengan campuran es—garam pada suhu 0 °C, kemudian dia alisis dengan kromatografi gas dan spektrometri massa (GC—MS). Pirolisis campuran plastik—tempurung kelapa menghasilkan produk utama alk na, alkena, dan alkohol, sedangkan pirolisis katalitik menghasilkan produk utama alk na, alkohol, eter aromatik dan asam karboksilat aromatik. Semakin banyak massa plan ik pada campuran swivel, volume hasil pirolisis semakin banyak. Penggunaan kat • lis zeolit alam asam mempercepat proses pirolisis, meningkatkan volume fraksi non air dan jumlah senyawa produk pirolisis. The use of plastic in human life effects the increase of plastic waste. The plas is that widely used is made of polyethylene. Meanwhile, the coconut production resu t coconut shell that consists of cellulose (36,3 %), lignin (28,3 %) and he cellulose (25,1 %) that potentially to be treated chemically. The aims of pyr•lysis of plastic—coconut shell mixture were to determine the effect of plastic¬coc nut shell composition and catalyst to the product of pyrolysis. Pyrolysis process was done to 60 g of plastic—coconut shell mixture by mass rati•1 : 5, 1 : 2, 1 : 1, 2 : 1 and 5: 1 at temperature 300 °C in a batch reactor. For cata ytic pyrolysis process, 5 g of acidic natural zeolite catalyst was added into the reac or. Nitrogen gas was flow into the reactor to get inert condition. The gas product con ti ensed by ice—salt mixture condensor at temperature 0 °C and then was analyzed by • s chromatography and mass spectrometry (GC—MS). Pyrolysis of plastic—coconut shell mixture produced alkane, alkene, and alto of and catalytic pyrolysis produced alkene, alcohol, aromatic ether and aromatic carboxylic acid as main products. More plastic in the mixture resulted more volume of Ion—water fraction liquid product. The use of catalyst shortened pyrolysis time incrr ased volume of non—water fraction product and numbers of compounds.
| Item Type: | Thesis (Undergraduate) |
|---|---|
| Subjects: | Q Science > QD Chemistry |
| Divisions: | Faculty of Science and Mathematics > Department of Chemistry |
| ID Code: | 31036 |
| Deposited By: | Mr UPT Perpus 1 |
| Deposited On: | 14 Nov 2011 07:39 |
| Last Modified: | 14 Nov 2011 07:39 |
Repository Staff Only: item control page