Hapsari , Sofia (2004) Pengaruh temperatur sintering terhadap karakter elektrolit pada sel bahan bakar Bi203 dengan bahan penstabil A1203. Undergraduate thesis, FMIPA UNDIP.
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 1846Kb | ||
| PDF 16Kb | |
| PDF 357Kb | |
| PDF 501Kb | |
| PDF 379Kb | |
| PDF 694Kb | |
| PDF 419Kb | |
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 630Kb | ||
| PDF 334Kb | |
| PDF 351Kb | |
| PDF 544Kb |
Abstract
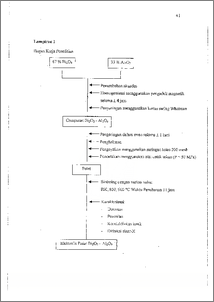
Telah dilakukan penelitian mengenai pengaruh temperatur sintering terhadap elektrolit padat sel bahan bakar B1203 dengan bahan penstabil Al203. Temperatur sintering menentukan terbentuknya struktur Bi203. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk menetapkan pengaruh temperatur sintering terhadap densitas, porositas, dan konduktivitas ionik elektrolit padat sel bahan bakar Bi203 dengan bahan penstabil Al203. Penambahan Al203 dan variasi temperatur sintering dimaksudkan agar dapat meningkatkan konduktivitas ionik Bi203 sehingga diperoleh elektrolit padat bismut oksida yang mempunyai konduktivitas ionik yang tinggi dan stabil pada temperatur operasi tertentu. Eksperirnen dilakukan mencampur 67 % Bi203 dan 33 % Al203 kemudian disintering dengan variasi suhu 800, 850, dan 900 °C waktu penahanan 11 jam. Setelah dihasilkan benda uji dari proses sintering, maka dilakukan karakterisasi, yaitu densitas, porositas, konduktivitas ionik, dan analisis difraksi sinar-X. Dari hasil penelitian didapatkan bahwa nilai konduktivitas ionik pada temperatur operasi 395 °C untuk sampel dengan suhu sintering 900 °C waktu penahanan 11 jam dapat meningkatkan konduktivitas ionik bismut oksida murni dari 5,47 x 10-7 S.criii menjadi 6,91 x 10-7 S.cm-'. Densitas yang diperoleh 6,2:364 g/cm3 dan porositas 7,6309 %. Hasil analisis difraksi sinar-X menunjukkan adanya senyawa 8-Bi203 dan A14131209. The effect of sintering temperature to the density, porosity, and ionic conductivity has been experimentally tested. The aim of the research is to deterthine the influence of the sintering temperature to density, porosity, and ionic conductivity. The research used bismuth oxide as the raw material with alumunium oxide as the dopant and the variation of sintering temperature to increase ionic conductivity. The aluminium oxide addition was 33 % mole with variation of sintering temperature at 800, 850, 900 °C and holding time 11 hours. The result showed that the measuring of ionic conductivity with operation temperature at 395 °C can increase the ionic conductivity of bismuth oxide from 5.47 x le s.ern- to 6.91 x 10-7 S.cm-I on 33 % mol aluminium oxide with sintering temperature at 900 °C and holding time 11 hours. Measurement of density was 6.2364 glcm3 or 87.74 % of theoretical density with porosity of 7.6309 %. X-Ray diffraction data showed that 8-Bi203 and Al4Bi209 were formed.
| Item Type: | Thesis (Undergraduate) |
|---|---|
| Subjects: | Q Science > QD Chemistry |
| Divisions: | Faculty of Science and Mathematics > Department of Chemistry |
| ID Code: | 30979 |
| Deposited By: | Mr UPT Perpus 1 |
| Deposited On: | 10 Nov 2011 15:01 |
| Last Modified: | 10 Nov 2011 15:01 |
Repository Staff Only: item control page