Zubaidi , Amin (2003) Pengaruh diameter partikel dan suhu kalsinasi terhadap dealuminasi zeolit alam Wonosari. Undergraduate thesis, FMIPA UNDIP.
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 1744Kb | ||
| PDF 16Kb | |
| PDF 357Kb | |
| PDF 453Kb | |
| PDF 367Kb | |
| PDF 651Kb | |
| PDF 374Kb | |
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 573Kb | ||
| PDF 322Kb | |
| PDF 357Kb | |
| PDF 650Kb |
Abstract
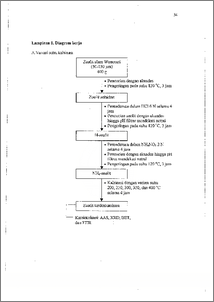
Dealuminasi zeolit alam telah dilakukan dengan maksud untuk meningkatkan rasio Si/A1, luas permukaan, dan kristalinitas. Proses dealuminasi diawali dengan perendaman zeolit dalam larutan HC1 6 N selama 4 jam dengan variasi diameter partikel 50 - 150, 150 - 250, dan 250 - 850 ptm, dicuci hingga netral, kemudiar. dikeringkan. Prosedur selanjutnya adalah sama tetapi menggunakan NH4NO3 2 N sebagai perendam. Zeolit kering dikalsinasi dengan variasi suhu 200, 250, 300, 350, dan 400 °C selama 4 jam dalam furnace. Hasil dikarakterisasi dengan AAS untuk menentukan rasio Si/Al. Sampel dengan rasio Si/Al tertinggi beserta zeolit alam dikarakterisasi menggunakan XRD untuk mengetahui kristalinitas, BET untuk mengetahui luas permukaan, dan FUR untuk mengetahui gugus yang terikat pada zeolit. Hasil penelitian menunjukkan dealuminasi terbaik terjadi pada diameter partikel 50 - 150 gm dan suhu kalsinasi 250 °C. Pada perlakuan tersebut terjadi peningkatan rasio Si/A1 dan 5,312 menjadi 26,857 yang menyebabkan perubahan kristal mengarah ke bentuk NH4-mordenit dengan luas permukaan 14,770 m2/g dan kristalinitas 13,425 % lebih tinggi dari zeolit alam. Dealumination on natural zeolit had been conducted in order to increase the Si/A1 ratio, surface area, and crystallinity. The dealumination process started by immersing zeolit in 6 N HC1 for 4 hours after treated to be powder as particle diameter as 50 — 150, 150 — 250, and 250 — 850 gm. Zeolite then been neutralized by aquadest washing and dried at 120 °C. Furthermore, the process is the same as before despite 2 N NH4NO3 as the immersing agent. Zeolite was going to be calcined under temperature variable as 200, 250, 300, 350, and 400 °C for 4 hours. Dealuminated zeolite then been characterized by AAS to determine Si/Al ratio. Next, sample with highest Si/Al ratio and natural zeolite were characterized by AAS, XRD, BET, and FIER to determine Si/A1 ratio, crystallinity and mineral composition, surface area and porosity, and the chemical bonding group. The experiment results show that at particle diameter 50 — 150 1.1m and calcination temperature of 250 °C, dealumination had increased the Si/AI ratio from 5.312 to 26.857, also transformed natural zeolit into Nth-mordenite with surface area as 14.770 m2.g-I and crystallinity 13.425 % higher than natural zeolite. This document is Undip Institutional Repository Collection. The author(s) or copyright owner(s) agree that UNDIP-IR may, without changing the content, translate the submission to any medium or format for the purpose of preservation. The author(s)1 o V r copyright owner(s) also agree that UNDIP-IR may keep more than one copy of this Submission for purposes of security, back-up and preservation. ( http:lleprints.undip.ac.id)
| Item Type: | Thesis (Undergraduate) |
|---|---|
| Subjects: | Q Science > QD Chemistry |
| Divisions: | Faculty of Science and Mathematics > Department of Chemistry |
| ID Code: | 30956 |
| Deposited By: | Mr UPT Perpus 1 |
| Deposited On: | 10 Nov 2011 12:16 |
| Last Modified: | 10 Nov 2011 12:16 |
Repository Staff Only: item control page