Saragih , Sonly Hamonangan (2003) Pengaruh pemanasan fosfolipid dari santan kelapa terhadap aktivitas permukaan. Undergraduate thesis, FMIPA UNDIP.
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 1522Kb | ||
| PDF 16Kb | |
| PDF 350Kb | |
| PDF 474Kb | |
| PDF 384Kb | |
| PDF 662Kb | |
| PDF 413Kb | |
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 468Kb | ||
| PDF 325Kb | |
| PDF 349Kb | |
| PDF 459Kb |
Abstract
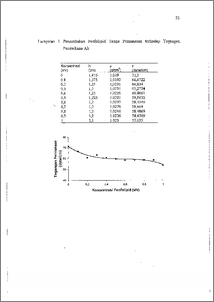
Fosfolipid dan santan kelapa merupakan zat pengemulsi yang potensial untuk dimanfaatkan dalam industri pangan sebagai zat pengemulsi altematif. Dalam dunia industri fosfolipid lebih dikenal dengan nama lesitin. Pemanasan terhadap lesitin komersial menyebabkan terjadinya perubahan warn menjadi kecoklatan, dan cenderung dianggap bahwa lesitin tersebut rusak. Perubahan tersebut juga mengubah aktivitas antarmuka lesitin. Penelitian akan menentukan pengaruh pemanasan fosfolipid dari emulsi santan kelapa terhadap aktivitas antarmuka udara-air. Aktivitas tersebut ditentukan melalui pengukuran tegangan permukaan air dengan penambahan fosfolipid. Pemanasan fosfolipid dilakukan dengan variasi temperatur 40 — 200 °C selama 40 menit untuk mengubah penampilan dan sifat permukaannya. Hasil pengukuran menunjukkan penambahan fosfolipid yang telah dipanaskan pada sub] 160 °C selama 40 menit menurunkan tegangan permukaan air lebih besar dibandingkan dengan penambahan fosfolipid tanpa pemanasan. Phospholipid from coconut milk is a potensial alternative emulsifier that can be use in food industry. Industry known phospholipid as a lecithin. Heated lecithin under certain condition caused browning color, make lecithin useless, and change its interface activity. Our research is concern to identify the effect of thermalized phospholipid from coconut milk to its surface activity. We examined surface tension of aqueous solution containing thermalized phospholipid to observe its surface activity Phospholipid has been heated under various temperatures from 40 to 200 °C for 40 minutes to alters it appearance and surface properties. The result showed significant decreasing of surface tension in aqueous solution containing thermalized phospholipid at 160 °C compare to those prepared with corresponding amounts of non thermalized phospholipid This document is Undip Institutional Repository Collection. The author(s) or copyright owner(s) agree that UNDIP-IR may, without
| Item Type: | Thesis (Undergraduate) |
|---|---|
| Subjects: | Q Science > QD Chemistry |
| Divisions: | Faculty of Science and Mathematics > Department of Chemistry |
| ID Code: | 30938 |
| Deposited By: | Mr UPT Perpus 1 |
| Deposited On: | 10 Nov 2011 09:51 |
| Last Modified: | 10 Nov 2011 09:51 |
Repository Staff Only: item control page