N u r h a d i , N u r h a d i (2003) Pengaruh impregnasi 2-merkaptobenzoliazol pada tanah diatome untuk adsorpsi logam kadmium (II) dalam medium air. Undergraduate thesis, FMIPA UNDIP.
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 1815Kb | ||
| PDF 16Kb | |
| PDF 369Kb | |
| PDF 493Kb | |
| PDF 452Kb | |
| PDF 698Kb | |
| PDF 384Kb | |
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 578Kb | ||
| PDF 327Kb | |
| PDF 373Kb | |
| PDF 503Kb |
Abstract
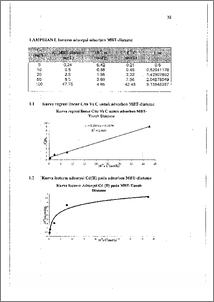
Adsorpsi merupakan salah satu metode penurunan kadar logam berat dalam perairan karena selain mudah dilakukan juga tidak memerlukan biaya tinggi dan hasilnya cukup memuaskan. Material alam maupun sintesis dengan berbagai modifikasi telah banyak digunakan sebagai adsorben salah satunya adalah tanah diatome. Kadmium(.II) diadsorpsi oleh adsorben karena kadmium(11) merupakan salah satu dari logam berat yang terdapat di lingkungan. Telah dibuat adsorben melalui impregnasi 2-Merkaptobenzotiazol (.MBT) pada tanah diatome setelah perlakuan fisikokimia meliputi pemanasan (80 °C) dalam campuran KMnO4-H2SO4, H2SO4 dilanjutkan HCl kemudian dilapisi dengan polistirena. Adsorben yang dihasilkan digunakan untuk adsorpsi Cd(II) dengan menggunakan sistem hatch-shaker selama 30 menit dalam medium air. Sebagai pembanding digunakan tanah diatome tanpa impregnasi. Isoterm adsorpsi Langmuir digunakan untuk menentukan kapasitas adsorpsi dan energi adsorpsi ion logam berat. Hasilnya menunjukkan bahwa adsorpsi ion logam pada tanah diatome yang terimpregnasi 2-Merkaptobenzotiazol diadsorpsi secara kimiawi dengan kapasitas adsorpsi 5,598 mg/g dan energi adsorpsi 25,736 kJ/mol. Sedangkan adsorpsi ion logam pada tanah diatome tanpa impregnasi diadsorpsi secara fisik dengan kapasitas adsorpsi dan energi adsorpsi berturut-turut 10,12 mg/g dan 20,75 knrnol. Sementara adsorpsi Cd(11) dalam medium air pada tanah diatome terimpregnasi optimum pada pH 6 sedangkan tanah diatome optimum pada pH 5. Adsorption is a method to deconcentration of heavy metal in aqueous medium because it is easy to use and it also doesn't need high cost and the result was contented. Both natural and syntetic materials with many modification are used as adsorbents. Cadmium(II) is adsorbed by adsorbents because cadmium is one of heavy metal which place in environment. An adsorbent has been prepared by impregnating 2- Mercaptobenzothiazole (MBT) on diatomaceous earth after physicochemical treatments include heating (80 °C) in KMna4-H2SO4 mixture followed by HCI addition, then coating with a layer polystyrena. The adsorbent can be used to adsorb Cd(II) by utilizing a batch-shaker for 30 minutes technique in aqueous medium. For comparison purpose, diatomaceous earth without impregnation was used too. Langmuir model for isotherm adsorption was applied to estimate the adsorption capacity and energy involved in the metal ion adsorption. Result showed that metal ion adsorption on 2-Mercaptobenzothiazol impregnated on diatomaceous earth was chemically adsorbed with adsorption capacity was 5.598 mg/g and adsorption energy was 25.736 kJ/mole. Whereas metal ion adsorption on diatomaceous earth without impregnation was physically adsorbed with adsorption capacity and adsorption energy were 10.12 mg/g and 21.04 kJ/mole, respectively. More over, adsorption of Cd(II) from aqueous solution on MBT¬diatomaceous earth was optimum at pH 6 whereas on diatomaceous earth was optimum at pH 5.
| Item Type: | Thesis (Undergraduate) |
|---|---|
| Subjects: | Q Science > QD Chemistry Q Science > QC Physics |
| Divisions: | Faculty of Science and Mathematics > Department of Chemistry |
| ID Code: | 30936 |
| Deposited By: | Mr UPT Perpus 1 |
| Deposited On: | 10 Nov 2011 09:41 |
| Last Modified: | 10 Nov 2011 09:41 |
Repository Staff Only: item control page