Wulandari , Eko Retno (2003) Preparasi elektrolitik lapisan film Zns pada permukaan plat aluminium melalui variasi potensial listrik eksternal. Undergraduate thesis, FMIPA UNDIP.
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 2300Kb | ||
| PDF 16Kb | |
| PDF 369Kb | |
| PDF 447Kb | |
| PDF 358Kb | |
| PDF 556Kb | |
| PDF 398Kb | |
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 511Kb | ||
| PDF 325Kb | |
| PDF 369Kb | |
| PDF 1329Kb |
Abstract
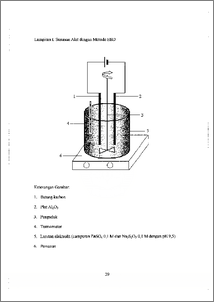
Lapisan film kalkogenida ZnS yang bersifat fotokonduktif memberikan banyak sekali kegunaan terutama untuk piranti optoelektronik. Hasil penelitian terdahulu melaporkan bahwa metode pengendapan elektrokimiawi (Electrochemical Bath Deposition, EBD) dapat diterapkan untuk preparasi CdS. Namun, hasil penelitian tersebut tidak memberitahukan hasil pengendapan elektrolitik untuk ZnS. Melalui penelitian ini, preparasi ZnS dilakukan berdasarkan metode EBD yang bertujuan untuk menentukan efek variasi potensial listrik eksternal terhadap karakter spektral lapisan film ZnS. Karakter spektral diungkapkan sebagai titik belok absorbansi energi gap Eg, dan sensitivitas absorbansi terhadap perubahan panjang gelombang AA/AX. Seng sulfida, ZnS, diendapkan dalam bentuk lapisan film pada permukaan substrat aluminium dari larutan ZnSO4 dan Na2S2O3. Larutan ZnSO4 sebagai sumber ion seng dan Na2S2O3 sebagai sumber ion sulfida. Sebelum dipakai sebagai substrat, aluminium dianodisasi terlebih dahulu dalam larutan HC1 0,2 M selama 1 jam. Pengendapan dilakukan di bawah variasi potensial listrik eksternal, yaitu —0,2; —0,4; —0,6; —0,7; dan —0,8 V. Lapisan film ZnS yang terbentuk dianalisis dengan XRD dan spektrofotometer UV—Vis reflektans. Difraktogram sinar—X membuktikan bahwa endapan yang terbentuk adalah ZnS. Hasil analisis dengan spektrofotometer UV—Vis reflektans menunjukkan pada variasi potensial listrik eksternal —0,4 V, lapisan film ZnS mencapai harga minimum, yaitu 320,2 nm yang berpadanan dengan Eg maksimum 3,87 eV. Sensitivitas AA/AX tertinggi pada variasi potensial listrik ekstemal —0,2 V, yaitu 2,415 x 107 m-1. The chalcogenide film layer ZnS that has photoconductive properties gives a lot of applications especially for optoelectronic devices. The last research reported a good result of CdS deposition by Electrochemical Bath Deposition (EBD) method, but it did not report the deposition of ZnS In this research, the preparation of ZnS was done by EBD method to determine the effect of external potential variation to the spectral characteristic of ZnS. The spectral characteristic is expressed by the point where an abrupt change in absorbance occurs A.8, band gap energy Eg, and absorbance sensitivity to wavelength change AAJAA.. Zinc sulfide, ZnS, was deposited as film layer on the aluminum surface from ZnSO4 and Na2S2O3 solution. Zinc sulfate, ZnSO4, was used as zinc ion source and sodium thiosulfate, Na2S2O3, was used as sulfide ion source. Aluminum plate has been anodically treated in 0.2 M hydrochloride acid solution during 1 hour before used. Electrochemical deposition has been carried out under the external potential variation of —0.2, —0.4, —0.6, —0.7, and —0.8 V. The film layer deposit was characterized by XRD and UV—Vis reflectant spectrophotometer. The X—ray diffi-actogram show that the deposit was really ZnS. The UV—Vis spectra show that for external potential —0.4 V, ZnS deposit gives minimum Xg of 320.2 urn which in accordance with maximum energy gap of 187 eV. The highest sensitivity AA/AX of ZnS deposit is 2.415 x 107m-I for external potential —0.2 V.
| Item Type: | Thesis (Undergraduate) |
|---|---|
| Subjects: | Q Science > QD Chemistry |
| Divisions: | Faculty of Science and Mathematics > Department of Chemistry |
| ID Code: | 30923 |
| Deposited By: | Mr UPT Perpus 1 |
| Deposited On: | 09 Nov 2011 16:00 |
| Last Modified: | 09 Nov 2011 16:00 |
Repository Staff Only: item control page