Yuliarni , Yuliarni (2003) Pengaruh suhu terhadap aktivitas serangan sulfat pada beton semen klas G-Abu Layang. Undergraduate thesis, FMIPA UNDIP.
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 2060Kb | ||
| PDF 14Kb | |
| PDF 370Kb | |
| PDF 470Kb | |
| PDF 392Kb | |
| PDF 524Kb | |
| PDF 523Kb | |
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 377Kb | ||
| PDF 322Kb | |
| PDF 384Kb | |
| PDF 373Kb |
Abstract
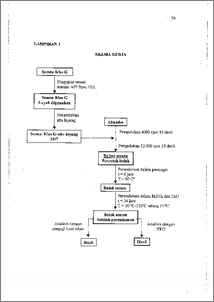
Proses sementasi pada operasi pemboran dilakukan dan permukaan tanah hingga kedalaman .sekitar 2500 meter, pada kedalaman tersebut terdapat gangguan-gangguan yang sering muncul, contohnya adalah perubahan suhu dan serangan sulfat. Telah dilakukan penelitian untuk mengetahui pengaruh suhu terhadap aktivitas serangan sulfat pada beton semen klas G-abu layang. Penambahan abu layang dilakukan untuk memperkaya kandungan silika sehingga gel C-S-H yang merupakan senyawa pengikat pada beton semakin banyak terbentuk. Penelitian dilakukan melalui beberapa tahapan, yaitu pembuatan beton berdasarkan standar American Petroleum Institute dimana bubur semen direndam dalam penangas selama 6 jam dengan suhu 60 °C dan perendaman beton dalam larutan H2SO4 0,05 M dilakukan selama 24 jam pada kisaran suhu 30 °C hingga 110 °C dengan interval 10 °C. Pengaruh sulfat terhadap semen klas G dengan dan tanpa penambahan abu layang dibandingkan untuk mengetahui perbedaan kuat tekan dan komposisi komponen mineral semen klas G. Karakterisasi hasil dilakukan dengan menentukan kuat tekan beton menggunakau alat penguji kuat tekan dan komposisi komponen mineral beton menggunakan metoda difraksi sinar X. Disimpulkan bahwa penambahan abu layang meningkatkan kemampuan menahan serangan sulfat. Kemampuan optimum beton dalam menahan serangan sulfat adalah pada suhu 70 °C, kuat tekan pada kondisi tersebut adalah 3675 lbs. Senyawa yang terbentuk hasil interaksi antara sulfat dengan komponen semen adalah ettringit dan taumasit. Cementing process of drilling operation is done from ground surface until the depth approximately 2500 meter where interferences occur, for example temperature and sulphate attack. The research effect of temperature to sulphate attack activity in G class cement-fly ash concrete had been done. The addition of fly ash was done to enrich silica content thereby C-S-14 gel as bound compound in concrete formed increased. The research was done through several steps, there were the making of concrete by American Petroleum Institute standard where the slurry immersed in water bath during 6 hours with temperature 60 °C and the immersion of the concrete into H2SO4 0,05 M was done during 24 hours with temperature between 30 °C and 110 °C with interval of 10 °C. The sulphate effect to G class cement with and without addition of fly ash were compared to know the difference of compressive strength and composition of mineral component of G class cement. Characterization of the results were done by determination the compressive strength using compressive strength tester and composition of mineral components of the concrete with X ray diffraction method. The results showed that the addition of fly ash to G-class cement increased the ability to overcome the sulphate attack. Optimum ability of the concrete to compensate for was at temperature 70 °C, with compressive strength at that condition 3675 lbs. Compounds formed as the interaction between sulphate and component of cement are dttringite and thaumasite. This document is Undip Institutional Repository Collection. The author(s) or copyright owner(s) agree that UNDIP-IR may, without changing the content, translate the S submission to any medium or format for the purpose of preservation. The author(Orr copyright owner(s) also agree that UNDIP-IR may keep more than one copy of this subthission for purposes of security, back-up and preservation. ( http://eprints.undip.ac.id)
| Item Type: | Thesis (Undergraduate) |
|---|---|
| Subjects: | Q Science > QD Chemistry |
| Divisions: | Faculty of Science and Mathematics > Department of Chemistry |
| ID Code: | 30913 |
| Deposited By: | Mr UPT Perpus 1 |
| Deposited On: | 24 Nov 2011 14:06 |
| Last Modified: | 24 Nov 2011 14:06 |
Repository Staff Only: item control page