Muflikhah , Muntoharoh (2005) Daya antibakteri senyawa non Alkaloid kulit kayu pulai gading (Alstonia scholoris, R. Brown) terhadap Staphyloccus aurus secara in vitro. Undergraduate thesis, FMIPA UNDIP.
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 1492Kb | ||
| PDF 17Kb | |
| PDF 357Kb | |
| PDF 463Kb | |
| PDF 376Kb | |
| PDF 541Kb | |
| PDF 444Kb | |
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 510Kb | ||
| PDF 324Kb | |
| PDF 391Kb | |
| PDF 448Kb |
Abstract
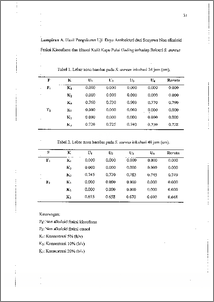
Pulai gading (Alstonia scholaris, R. Brown) sudah sejak lama digunakan sebagai obat kulit dan sakit perut seperti diare, antara lain disebabkan oleh Staphylococcus aureus. Alkaloid yang dipercaya mempunyai khasiat sebagai obat, ternyata tidak dapat menghambat pertumbuhan S. aureus. Penelitian ini bertujuan mengisolasi senyawa non alkaloid fraksi kloroform than etanol kulit kayu A. scholaris dan menguji aktivitas antibakterinya terhadap S. aureus secara in vitro. Pemisahan senyawa alkaloid dan non alkaloid ekstrak fraksi kloroform dan etanol kulit kayu A. scholaris dilakukan dengan ekstraksi jalur khusus alkaloid menurut cara Adel Zamri (1989), sedangkan uji antibakteri dilakukan dengan metode paper disk pada konsentrasi 5%, 10% dan 20% (b/v) untuk masing¬masing fraksi. Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa pada konseniraii 5% dan 10% (b/v) kedua fraksi tidak menyebabkan hambatan terhadap pertumbuhan S. aureus. Pada konsentrasi 20% (b/v), senyawa non alkaloid fraksi kioroform menyebabkan hambatan yang lebih besar dan berbeda nyata dibandingkan dengan senyawa non alkaloid fraksi etanol. Senyawa non alkaloid fraksi kloroform dan etanol bersifat bakteriostatik terhadap S. aureus. Pulai gading (Alstonia scholaris, R. Brown) has been used as a skin and diarrhoea medicine since many years, Staphylococcus aureus was a bacteria which has known as one of diarrhoea causing agents. The alkaloid compounds has a medicinal activity, but it can't inhibit S. aureus growth. The aims of this research were to isolate ethanolic and chloroform fraction of non alkaloid compounds from A. scholaris bark and examined the antibacterial activities to S. aureus in vitro. The compounds separation was done by Adel Zamri extraction method (1989), while the antibacterial activities determined by paper disk method in the concentrations of 5%, 10% and 20% (w/v) for each fraction. The results showed that the non alkaloid compounds of ethanolic and chloroform fraction were caused no inhibition on the S. aureus growth in the concentrations of 5% and 10% (w/v). On the concentration 20°(o (w/v), non alkaloid compounds of chloroform fraction give the larger inhibition activity than ethanolic non alkaloid compounds and significantly different. Ethanolic and chloroform fraction of non alkaloid compounds showed a bacteriostatic activity on S. aureus. vii
| Item Type: | Thesis (Undergraduate) |
|---|---|
| Subjects: | Q Science > QD Chemistry |
| Divisions: | Faculty of Science and Mathematics > Department of Chemistry |
| ID Code: | 30877 |
| Deposited By: | Mr UPT Perpus 1 |
| Deposited On: | 08 Nov 2011 13:17 |
| Last Modified: | 08 Nov 2011 13:17 |
Repository Staff Only: item control page