Kumoro , Ibnu (2002) Pengaruh temperatur, garam N2CL dan sukrosa terhadap konsentrasi miselisasi kritis larutan fosfolipid dari emulsi santan kelapa. Undergraduate thesis, FMIPA UNDIP.
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 1553Kb | ||
| PDF 17Kb | |
| PDF 363Kb | |
| PDF 507Kb | |
| PDF 372Kb | |
| PDF 609Kb | |
| PDF 401Kb | |
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 547Kb | ||
| PDF 339Kb | |
| PDF 370Kb | |
| PDF 410Kb |
Abstract
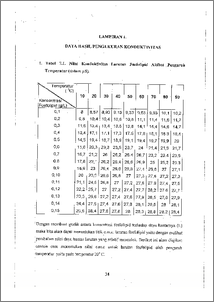
Santan kelapa merupakan ernulsi alam yang stabil. Hal ini menunjukkan bahwa emulsifier dalam santan, yaitu fosfolipid, potensial untuk dimanfaatkan dalam industri pangan. Namun harga konsentrasi miselisasi kritisnya (c.m.c.) harus diketahui terlebih dahulu, karena harga ini menentukan keefektifan dan keefisienan penggunaannya. Untuk itu, tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah menentukan bagainiana pengaruh temperatur, garam NaCI dan sukrosa terhadap harga c.m.c. lartitan fosfolipid. Metode penentuan c.m.c. yang digunakan adalah metode konduktometri. Pengaruh temperatur diukur dengan cara mengamati perubahaan nilai c.m.c. pada berbagai variasi temperatur yaitu pada temperatur 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, dan 90 °C. Sedangkan pengaruh NaC1 dan sukrosa ditentukan dengan cara mengarnati perubahan nilai c.m.c. pada berbagai konsentrasi dari garam NaCI dan sukrosa yaitu pada konsentrasi 0; 0.1; 0.2; 0.3; 0.4; dan 0,5 mg/L. Hasil eksperimen menunjukkan bahwa nilai c.m.c. akan naik dengan naiknya temperatur sistem dengan rata-rata kenaikan sebesar 11,79 % untuk tiap kenaikan temperatur sebesar 10 °C. Untuk pengaruh garam NaCI, kenaikan konsentrasinya akan menurunkan c.m.c. yaitu dengan rata-rata penurunan sebesar 14,71 % untuk setiap kenaikan konsentrasi NaC1 sebesar 0,1 mg/L. Sedangkan dengan kenaikan konsentrasi sukrosa akan menurunkan nilai c.m.c dengan rata-rata penurunan 8,69 % untuk setiap kenaikan konsentrasi sukrosa sebesar 0;1 mg/L. A coconut milk is a stable natural emulsion. It indicates that the emulsifier in coconut milk, which is known as phospholipid, is potential to use in food industry. Meanwhile, critical micelle concentration (c.m.c.) of phospolipid solution must be determined first, because this value depended the effectivity and efficiency it utilization. Because of that, the aim of this experiment is to find out effect of temperature, NaCl and sucrose concentration on c.m.c. value of phospholipid solution. The determination of c.m.c. is using conductivity method. Temperature effect was determined by observing the changes of c.m.c. value under temperature variation of 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80 and 90 ° C. While effect of NaC1 and sucrose was determined by observing the change of c.m.c. value under NaC1 and sucrose concentration variation of 0,1; 0,2; 0,3; 0,4 and 0,5 mg/L. Results showed that increasing temperature would increase c.m.c. value with the increasing average is 11,79 % every 100 C temperature increase. The increasing NaC1 concentration would decrease c.m.c. value with the decreasing average is 14,71% every 0,1 gIL of NaC1 salt concentration increase. While increasing sucrose concentration would decrease c.in.c. value with the decreasing average is 8,69 % every 0,1 g/L of sucrose concentration increase.
| Item Type: | Thesis (Undergraduate) |
|---|---|
| Subjects: | Q Science > QD Chemistry |
| Divisions: | Faculty of Science and Mathematics > Department of Chemistry |
| ID Code: | 30845 |
| Deposited By: | Mr UPT Perpus 1 |
| Deposited On: | 24 Nov 2011 14:06 |
| Last Modified: | 24 Nov 2011 14:06 |
Repository Staff Only: item control page