Ruminingsih , Ruminingsih (2000) Mengatasi interferensi Fosfat pada penentuan konsentrasi Kalsium secara Spektrometri serapan Atom nyala. Undergraduate thesis, FMIPA UNDIP.
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 1497Kb | ||
| PDF 15Kb | |
| PDF 365Kb | |
| PDF 427Kb | |
| PDF 359Kb | |
| PDF 657Kb | |
| PDF 440Kb | |
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 514Kb | ||
| PDF 341Kb | |
| PDF 340Kb | |
| PDF 418Kb |
Abstract
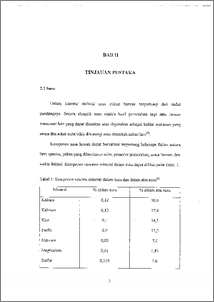
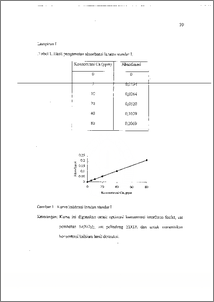
Adanya fosfat dalam sampel kalsium dapat menggangu penentuan konsentrasi kalsium secara spektrometri serapan atom nyala. Gangguan ini dapat diatasi dengan menambahkan stronsium sebagai zat pembebas atau EDTA sebagai zat pelindung atau menggunakan suhu nyala yang lebih tinggi. Telah dilakukan optimasi konsentrasi terhadap stronsium dan EDTA. Konsentrasi stronsium optimum 1,2 % dan konsentrasi EDTA optimum 500 ppm. KonSentrasi optimum ini ditambahkan dalam larutan kalsium hasil destruksi susu bubuk. Konsentrasi kalsium yang tertulis claim label 1700 mg/100 g susu bubuk. Tanpa penambahan stronsium atau EDTA, kadar kalsium yang terukur 1431 mg/ 100g (pungut ulang 84,18 %). Pada penambahan 1,2 % Sr(1\103), kalsium yang terukur 1710 mg/-100g (pungut ulang 100,58 %). Stronsium bereaksi dengan fosfat sehingga kalsium dapat diatomkan. Penambahan 500 ppm EDTA kadar kalsium yang terukur 1685 mg/100 g (pungut ulang 99,11 %). Garam EDTA dengan kalsium membentuk senyawa kompleks Ca-EDTA yang mudah diatomkan. Pada penggunaan suhu nyala yang lebih tinggi kadar kalsium yang terukur 1347,3 mg/100 g (pungut ulang 79,25%). Hasilnya lebih kecil karena kalsium dalam nyala terionisasi pada suhu tinggi. Dari hasil penelitian dapat disimpulkan bahwa stronsium atau EDTA dapat digunakan untuk mengatasi interferensi fosfat, sedangkan penggunaan suhu nyala yang lebih tinggi kurang efektif untuk mengatasi interferensi tersebut. The presence of phosphat in sample of calcium can interfere the determination of calcium concentration by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. This interference could be solved by addition of strontium such as releasing agent or EDTA such as protective agent or by using higher temperature.flarne. It has been done optimation of strontium and EDTA concentration. Optimum concentration strontium was 1.2 % and optimum concentration EDTA was 500 ppm. This optimum concentration was used in to calcium solution that Was resulted from powder milk destruction. The calcium concentration written on label was 1700 mg/100 g of powder milk. Without addition of strontium or EDTA, the measured calcium concentration was 1431 mg/100 g (recovery $4.18 %). The addition of 1.2 % Sr(NO3), measured calcium concentration was 1710 me100 g.(recovery 100.58 %). Strontium reacted with phosphat so calcium can be atoMized. By addition 500 ppm EDTA, the measured calcium was 1685 mg/100 g (recovery 99.11 %). EDTA and calcium forrned complex Ca-EDTA which was easily atomized. In using higher temperature flame, the measured calcium concentration was 1347.3 mg/100 g (recovery 79.25 %). The result was less because the calcium atoms were ionized by high temperatufe: • • Frofn the research can be concluded that strontium or EDTA could be used to solve interference of thisphat, and that using the higher temperature flame was less effective to solve this interference.
| Item Type: | Thesis (Undergraduate) |
|---|---|
| Subjects: | Q Science > QD Chemistry |
| Divisions: | Faculty of Science and Mathematics > Department of Chemistry |
| ID Code: | 30768 |
| Deposited By: | Mr UPT Perpus 1 |
| Deposited On: | 07 Nov 2011 09:14 |
| Last Modified: | 07 Nov 2011 09:14 |
Repository Staff Only: item control page