Ernasari , Susi (1998) Pengaruh terhadap potensial Galvanik sensor kelembaban Mangan Dioksida. Undergraduate thesis, FMIPA UNDIP.
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 1263Kb | ||
| PDF 16Kb | |
| PDF 390Kb | |
| PDF 427Kb | |
| PDF 344Kb | |
| PDF 519Kb | |
| PDF 367Kb | |
| PDF Restricted to Repository staff only 496Kb | ||
| PDF 325Kb | |
| PDF 331Kb | |
| PDF 424Kb |
Abstract
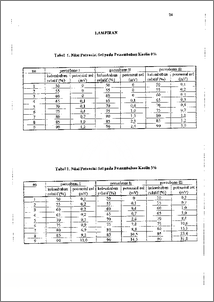
Elektrolit Mangan Dioksida (EMD) telah lama digunakan sebagai katoda pada baterai karena atom oksigennya mampu berikatan dengan 1-1÷ yang berasal dan molekul air. Dengan kata lain MnO2mampu merespon adanya kelembaban di lingkungan sekitar secara elektrokimia. Apabila Mn02 dihubungkan dengan suatu elektroda yaitu Cu dan C diketahui bahwa reaksi kimia yang dihasilkan mampu menimbulkan potensial Dari sifat Mn02 yang mampu merespon adanya kelembaban udara tersebut, maka Mn02 dapat dijadikan sebagai komponen utama elemen sensor kelembaban. Seiring dengan perkembangan ilmu pengetahuan diketahui bahwa dengan mencampurkan jenis lempung tertentu ke dalam Mn02 ternyata dapat meningkatkan kerja sensor. Kaolin adalah salah satu jenis lempung yang mampu mengadsorbsi air. Dalam penelitian ini dilakukan percobaan dengan menggunal: ,n kaolin sebagai aditif yang ditambahkan pada elemen sensor sehingga diperoleh gambaran mengenai hubungan variasi kaolin dengan Mn02 secara terperinci. Dari penambahan kaolin yang bervariasi dapat diperoleh konsentrasi optimum kaolin yang juga menunjukkan kerja sensor yang maksimal. Dengan menggunakan konsep reaksi redoks pada sistem sel galvani yang diterapkan pada elemen sensor Mn02-kaolin maka reaksi redoks yang terjadi pada anoda dan katoda akan menimbulkan beda potensial. Potensial yang dihasilkan dijadikan parameter kemampuan kerja sensor. Metode yang diterapkan dalam penelitian ini adalah dengan menernpatkan sistem sensor Mn02-kaolin sebagai elektrolit padat pada sel galvani dengan cara menjepitkan elektrolit di antara elektroda tembaga dan karbon kemudian memasuldmn rangkaian tersebut ke dalam ruang uji pada kelembaban yang divariasi. Dengan memasang multimeter pada modus voltase, potensial sel sebagai fiingsi kelembaban akan dapat dibaca Dari hasil eksperimen didapatkan bahwa pada kelembaban relatif 90% dengan penambahan kaolin 0,5,10,15,20 dan 25% beda potensial yang dihasilkan berturut-turut 2,5; 19,433; 44,7; 27,767; 3,933 dan 2,167 mV. Dari data lengkap hasil eksperimen diketahui bahwa dengan naiknya kelembaban yang diikuti dengan naiknya nilai Esei menunjukkan semakin banyaknya uap air yang dapat teradsorbsi pada kelembaban tinggi. Sehingga dapat disimpulkan bahwa penambahan kaolin yang optimum adalah pada 10%. Electrolytic Manganese Dioxide (ErviD) has been used as a dry battery cathode because its oxygen atom could bind the 1-1+ originating from water molecules. Otherwise, manganese dioxide would respond electrochemically to 1120 in the ambient atmosphere. When Mn02 was connected with electrodes namely Cu and C , it was known that the reaction get involved could produced electrical potential. From the nature of the Mn02 that respond moisture from the ambient air, so Mn02 has an ability as a main component of the humidity sensor. Recently the development in science, has been found that by mixing certain clay into Mn02, the treatment can increase the performance of the sensor. Kaolin is one of the clay that can adsorb water. In this research, experiment by using kaolin as additives in the element sensor has been done, so the description about the •orrelation between varied kaolin with Mn02 will be obtained. From the addition, the kaolin optimum concentration that show the maximum performance of the sensor has been attained. By using the redox reaction at the galvanic cell system that applied to the sensing element Mn02-kaolin, the reaction happened at the anode and cathode will produce the potential difference. This potential defined as performance parameter of the humidity sensor. The method applied in this research was using Mn02-kaolin sensor's system as a solid electrolyte by inserting it between Cu and C electrodes then put it in a test chamber where the humidity could be varied. By setting multimeter at the voltage mode, the cell potential as a function ofhumidity will be able to read. From the experiment results, at the 90% relative humidity by adding 0.5.10.15.20 and 25% kaolin,the cell potentials generated were 2.5; 19.433; 44.7; 27.767; 3.933 and 2.167 mV respectively. From the overall data, it was found that increasing humidity followed by increasing cell potential showed a lot of water vapor can be adsorbed at the high humidity. So the conclusion can be drawn that the optimum addition is at 10% kaolin.
| Item Type: | Thesis (Undergraduate) |
|---|---|
| Subjects: | Q Science > QD Chemistry |
| Divisions: | Faculty of Science and Mathematics > Department of Chemistry |
| ID Code: | 30709 |
| Deposited By: | Mr UPT Perpus 1 |
| Deposited On: | 04 Nov 2011 14:56 |
| Last Modified: | 04 Nov 2011 14:56 |
Repository Staff Only: item control page