Ashammam, Aisha Abduljalil (2011) THE EFFECT OF HALOTHANE INHALATIONAL ANAESTHETICS ON LIVER CELLS(Experimental Study of Halothane Toxic Effect in BALB C Mice). Masters thesis, Diponegoro University.
| PDF (Chapter 7) - Published Version 91Kb | |
| PDF (Chapter 6) - Published Version 132Kb | |
| PDF (Chapter 1) - Published Version 170Kb | |
| PDF (Chapter 5) - Published Version 479Kb | |
| PDF (Chapter 4) - Published Version 148Kb | |
| PDF (Chapter 3) - Published Version 110Kb | |
| PDF (Chapter 2) - Published Version 178Kb | |
| PDF (Cover) - Published Version 220Kb | |
| PDF (Reference) - Published Version 118Kb | |
| PDF (Appendix) - Published Version 884Kb |
Official URL: http://www.mbiomedik.undip.ac.id/
Abstract
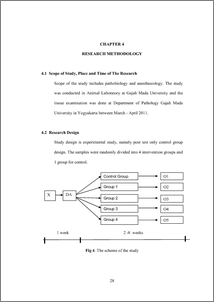
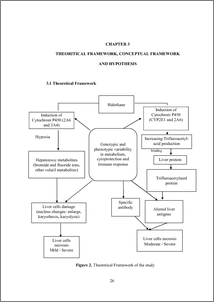
Background: Adverse effects of halothane on the liver range from liver dysfunction to hepatitis, and are more frequent following repeated use. Medical personals are in risk of chronic exposure of wasted halothane. However, there are limited literatures about this effect based on time exposure. Objectives: To identify and analyze the liver cells changes of halothane exposure to liver cells of Balb/C mice. Methods: This experimental study used randomized post-test only control group design in 30 male BalbC mice given 0.011 mg/weight halothane 3 hours daily for two weeks (group 1), four weeks (group 2), six weeks (group 3), six weeks followed by 2 weeks of halothane free (group 4), and without exposure (control group). The liver tissues were HE stained and observed for enlarge, karyorhexis, and karyolisis of the nucleus. Immunohistochemistry was undertaken to count the percentage of cytocrome-P450 stained brown colour and scored based on its intensity. Results: The difference among groups and between each group were statistically significant (p< 0.05), except between group 2 and 4 (p = 0.078), and between group 3 and 4 (p = 0.522). The difference of cytocrome-P450 expression among groups was not statistically significant (p = 0.266). Conclusion: There was statistically significant difference of abnormal liver cell nucleus changes in groups with different time of halothane exposure (p = 0.000) while no statistically significant difference of cytocrome-P450 expressions (p = 0.266) was found. The nucleus changes were gradually increased with the time of exposure. KEYWORDS: Halothane, liver cell nucleus changes, cytocrome-P450
| Item Type: | Thesis (Masters) |
|---|---|
| Subjects: | R Medicine > R Medicine (General) |
| Divisions: | School of Postgraduate (mixed) > Master Program in Biomedical Science |
| ID Code: | 30682 |
| Deposited By: | INVALID USER |
| Deposited On: | 04 Nov 2011 12:08 |
| Last Modified: | 04 Nov 2011 12:08 |
Repository Staff Only: item control page